How Can You Prevent Overheating in Your Pulse Induction Detector?
Pulse Induction (PI) detectors are widely used in metal detection and non-invasive inspections. They work by briefly connecting a coil to a battery, creatin
g high-current pulses. The frequency of these pulses can vary, but lower frequencies mean more power.To avoid overheating and save battery life, PI detectors run at a 4% duty cycle. This means they are on for a short time and off for a longer time.
ragraph -->The coil’s resistance is key to controlling the pulse’s decay. It’s important to dampen the pulse correctly for the best results. Keeping the temperature right and managing power is crucial for these detectors to work well over time.
Understanding pulse induction technology helps prevent overheating. By monitoring temperature and protecting the circuit, users can keep their detectors safe. We’ll explore the main parts, how they work, and how to manage temperature to avoid overheating.
Understanding Pulse Induction Technology Basics
Pulse induction (PI) metal detectors are better than traditional VLF models for finding explosives, contraband, and underground utilities. They use electromagnetic induction to find metal, even in tough soil where VLFs fail.
Transmitter and Receiver Components
A PI metal detector has a transmitter that sends out quick, high-voltage pulses. These pulses create eddy currents in metal objects, which the receiver coil can pick up. The receiver controls the pulse to avoid overload.
Sampling Circuit Operation
The sampling circuit is key in a PI metal detector. It boosts the signal by 1,000 times and samples it at zero. This gives the integrator the data it needs.
Integration System Function
The integrator turns the sampled signals into a DC voltage. Its speed determines how fast the detector responds. This helps PI devices spot metal objects well, making them useful in many fields.
PI detectors might not discriminate as well as VLFs. But, they excel in mineralized soil. This makes them essential in explosives detection, contraband screening, and underground utility mapping.
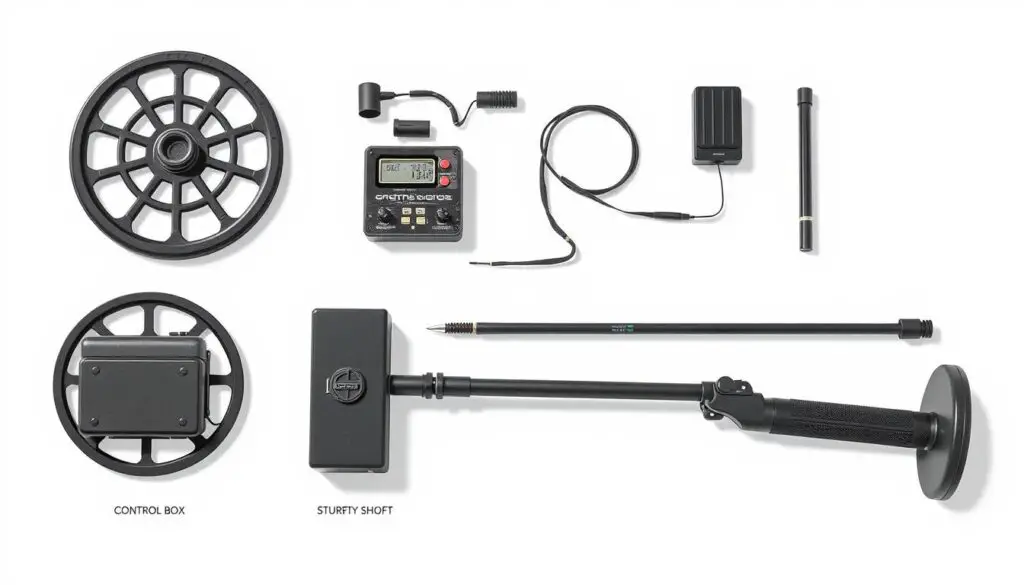

Common Causes of Overheating in Detection Equipment
Treasure hunting, archeological surveys, and void detection all use detection equipment. These devices can overheat, leading to early failure and downtime. It’s key to know why they overheat to keep them working well and lasting longer.
One big reason for overheating is using the equipment for a long time. Devices like pulse induction detectors get very hot when used non-stop. This heat can damage the insulation in motors, shortening their life. For every 10°C of temperature increase, the insulation’s life is cut in half.
High temperatures in the environment also cause overheating. In hot places, the equipment works harder, making more heat and possibly failing. Not having enough air to cool the equipment makes things worse.
- Insulation degradation in motors due to temperature increases
- Inadequate protection methods focusing solely on current supply rather than internal temperature
- Overheating as a major cause of premature motor failures
To solve these problems, we need to watch the temperature closely and protect the circuits well. By monitoring the equipment’s temperature and taking steps to prevent overheating, we can keep our tools working well for a long time.

Critical Temperature Monitoring Systems
Keeping the right temperature is key for Pulse Induction Detectors and other security gear to work well. Advanced systems watch the temperature closely to avoid overheating and breakdowns.
Thermistor Implementation
Thermistors are used to check the temperature in motors. They are simple devices put in the motor’s windings. Usually, three or six thermistors are used, one for each phase.
Some systems have two sets of thermistors. This gives both a warning and a trip signal for overheating protection.
Temperature Sensing Mechanisms
The Siemens SIRIUS 3RN2 thermistor motor protection relay is a smart choice for overheating protection. It comes in different setups, including automatic, manual, and remote reset. These systems use advanced sensors to watch the temperature closely and act fast when needed.
Heat Distribution Patterns
It’s important to know how heat spreads in Pulse Induction Detectors and metal detection gear. Sensors placed right can spot hot spots and send alerts. This helps in fixing problems early and keeps the equipment running smoothly.
Regular checks with thermal imaging and vibration analysis help understand the equipment’s health. This way, security scanning and metal detection experts can keep their Pulse Induction Detectors in top shape. This protects their investment and keeps their services running without a hitch.
Pulse Induction Detector Circuit Protection Methods
Keeping a Pulse Induction (PI) metal detector cool is key for safe use. These detectors are used for checking materials without damage. They need strong protection to avoid overheating issues.
One way to prevent overheating is by using special circuits. These circuits watch the temperature and cut off power when it gets too high. This stops the detector from getting too hot.
The system also controls the cooling fan and alerts the user if it gets too hot. This way, the detector stays safe and works well, even in tough conditions.